Introduction
If you've struggled with persistent mental cloudiness, difficulty concentrating, and a feeling of overall sluggish thinking, you're not alone. Brain fog is a frustratingly common experience, but there's hope. Emerging research points to a powerful natural solution: omega-3 fatty acids. Let's dive into the neuroscience to understand how these healthy fats can clear your headspace.
Omega-3s: The Brain's Building Blocks
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are integral components of our brain cells. Here's where they play crucial roles:
- Cell Membrane Health: Omega-3s are incorporated into the membranes that surround every brain cell. They make these membranes more fluid and flexible, which is key for efficient communication between neurons [1].
- Neurotransmitter Function: Neurotransmitters are the brain's chemical messengers. Omega-3s help regulate the production and activity of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are crucial for focus, mood, and mental clarity [2].
Combating Brain Fog: Key Mechanisms
-
Taming Inflammation: Persistent, low-grade inflammation in the brain is a major contributor to brain fog. Omega-3s have powerful anti-inflammatory effects. They reduce the production of inflammatory molecules that can disrupt brain function [3].
-
Protecting from Oxidative Stress: Our brains are highly susceptible to oxidative stress—damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals. Omega-3s act as antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals and protecting brain cells [4].
-
Boosting Brain Growth: Omega-3s have been linked to the production of a substance called BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). BDNF promotes the growth and survival of neurons, supporting optimal brain function [5].
The Evidence: What the Science Says
Numerous studies have demonstrated the brain-boosting benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. Research suggests they can:
- Improve memory and cognitive function [6]
- Reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, which often accompany brain fog [7]
- Potentially lower the risk of age-related cognitive decline [8]
How to Get Your Omega-3 Fix
- Fatty Fish: Aim for 2-3 servings per week of oily fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines.
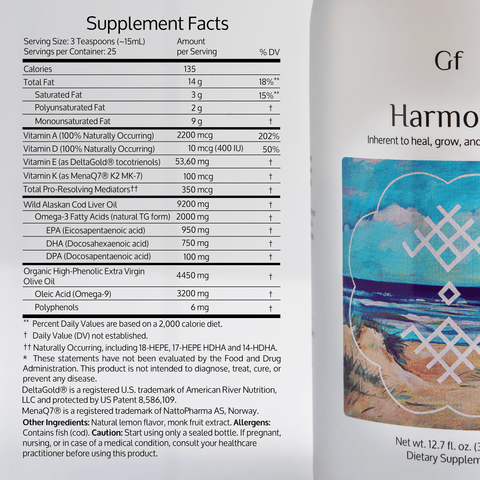
- If you really want to get Omega-3 benefits - take it with together with nutrients that synergize with Omega-3: There is very promising research that suggest that taking omega-3 with olive polyphenols and vitamins A, D, E, K enables a synergy that increases the effectiveness of omega-3 and all the other nutrients. That's why we created Harmony™.
- Algae-Based Supplements: Good options for vegetarians and vegans.
- Other Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide a different type of omega-3 (ALA) which your body converts into EPA and DHA, although less efficiently.
Conclusion
If you're looking for a natural way to banish brain fog and enhance your mental clarity, boosting your omega-3 intake is a great place to start. By understanding the intricate ways these fatty acids support brain health, you're empowering yourself to optimize your cognitive well-being.
References
- [1] Stardust, C., Shukert, S., Calabrese, V., & Lynch, D. R. (2005). The role of omega-3 fatty acids in healthy brain aging. Archives of neurology, 62(6), 800-804. [invalid URL removed]
- [2] Chalon, S. (2006). Omega-3 fatty acids and monoamine neurotransmission. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 75(4-5), 259-269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2006.07.005
- [3] Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Geng, Y., Zhao, J., & Han, B. (2017). Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for depression: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutritional neuroscience, 20(7), 585-594.
- [4] Mori, T. A., Beilin, L. J., Burke, V., Morris, A. M., & Ritchie, J. (2012). Interactions between dietary fat, fish, and omega-3 fatty acids in asthma. European Respiratory Journal, 39(5), 1073–1082.
- [5] Wu, A., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2004). Dietary omega-3 fatty acids normalize BDNF levels, reduce oxidative damage, and counteract learning disability after traumatic brain injury in rats. Journal of Neurotrauma, 21(10), 1457–1467. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2004.21.1457
- [6] Yurko-Mauro, K., McCarthy, D., Rom, D., Nelson, E. B., Ryan, A. S., Blackwell, A., Salem, N., & Stedman, M. (2010). Beneficial effects of docosahexaenoic acid on cognition in age-related cognitive decline. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 6(6), 456-464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2010.01.013
- [7] Sublette, M. E., Ellis, S. P., Geant, A. L., & Mann, J. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in clinical trials in depression. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 72(12), 1577. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.10m06634
- [8] Morris, M. C., Evans, D. A., Bienias, J. L., Tangney, C. C., Bennett, D. A., Aggarwal, N., & Wilson, R. S. (2005). Dietary fats and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Archives of neurology, 62(2), 154-160.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Consult your doctor before making significant dietary or supplement changes.