When we think about Omega-3 fatty acids, we often associate them with heart health or reducing inflammation. But did you know that Omega-3s play a vital role in mental health as well? Emerging research links Omega-3 deficiency not only to brain fog but also to mood disturbances and mental disorders like anxiety and depression. Let’s explore how a lack of Omega-3s impacts your brain, mood, and mental well-being.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Why Are They Important?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that your body cannot produce on its own, meaning you need to obtain them from your diet. There are three main types of Omega-3s: ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). While ALA is found in plant-based sources, EPA and DHA, which are crucial for brain function, are mostly found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as fish oil supplements.
DHA is a structural component of brain cell membranes, while EPA helps manage inflammation and neurotransmitter function. Together, they support cognitive health, mood regulation, and overall mental well-being.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency
Before diving into the mental health effects, it's helpful to recognize some common signs of Omega-3 deficiency:
- Brain Fog: Difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, and slow cognitive processing are key indicators.
- Fatigue: Low energy levels, despite adequate sleep, may signal that your body is lacking vital nutrients like Omega-3s.
- Dry Skin: Omega-3s help maintain skin’s moisture, so dry, flaky skin may suggest a deficiency.
- Joint Pain: Omega-3s’ anti-inflammatory properties help keep joints lubricated, and their absence can lead to discomfort.
If these symptoms sound familiar, it's time to explore how a lack of Omega-3s may be impacting your mental health.
The Connection Between Omega-3 Deficiency and Mental Health

1. Depression and Anxiety
There’s growing evidence that Omega-3 deficiency is linked to increased rates of depression and anxiety. EPA, in particular, is known for its anti-inflammatory effects, which can help reduce the inflammation linked to mood disorders. Studies have shown that people with depression often have lower levels of Omega-3s in their blood.
A 2016 meta-analysis published in Translational Psychiatry revealed that Omega-3 supplementation, particularly EPA, had a positive effect on reducing symptoms of depression, especially in those with severe cases (source). While Omega-3s are not a cure for depression, they can be an important complementary treatment for improving mood and emotional stability.
2. Cognitive Decline and Brain Fog
Omega-3s are vital for maintaining cognitive function throughout life. DHA, in particular, is essential for the development and maintenance of the brain's structure and function. A deficiency in DHA can lead to cognitive issues, including brain fog, slower reaction times, and memory problems.
A study in the Nutrients - international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of human nutrition found that individuals with higher DHA levels were less likely to experience cognitive decline as they aged, suggesting that DHA may protect against brain aging and memory loss (source).
3. ADHD and Learning Disabilities
Omega-3s play a crucial role in early brain development. Research has shown that children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) often have lower blood levels of Omega-3s. Supplementing with Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, has been found to improve attention, focus, and behavior in children with ADHD.
A study published in Neuropsychopharmacology demonstrated that children with ADHD who were supplemented with Omega-3s saw significant improvements in cognitive function and behavior compared to those who were not supplemented (source).
4. Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia
Some research suggests that Omega-3s may also play a role in managing more severe mental disorders, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. These conditions have been linked to increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, and Omega-3s’ anti-inflammatory properties can help mitigate these effects.
A study in Archives of General Psychiatry found that individuals with bipolar disorder who took Omega-3 supplements experienced longer periods of mood stability and fewer relapses (source). Similarly, Omega-3 supplementation has been explored as a potential treatment option for schizophrenia, with promising results in reducing symptoms like delusions and hallucinations.
Omega-3 Supplementation: A Key for Mental Wellness
If you suspect that your diet is lacking in Omega-3s, supplementation may be a practical solution. Fish oil, krill oil, and algae-based Omega-3 supplements provide the essential EPA and DHA your brain needs for optimal functioning.
- Fish Oil: A widely available supplement that contains both EPA and DHA.
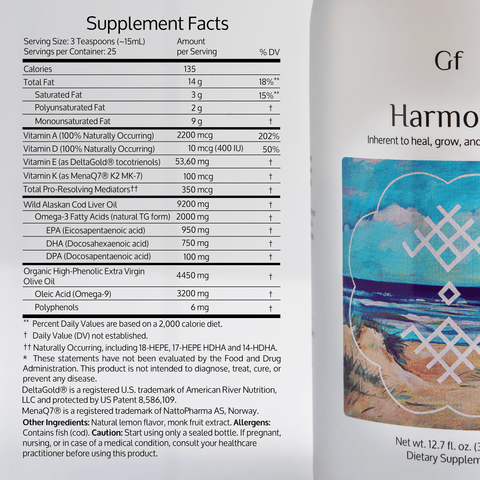
- Cod Liver Oil: Another source rich in Omega-3s that also includes antioxidants like astaxanthin. Check out our own Harmony™ for cod liver oil combined with other high-quality ingredients.
- Algae-Based Omega-3s: Ideal for vegetarians and vegans, providing a sustainable source of DHA and EPA without fish.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the right dosage and ensure that Omega-3 supplementation is right for your needs.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential not only for physical health but also for mental and emotional well-being. From combating brain fog and cognitive decline to alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety, Omega-3s play a critical role in maintaining your mental health. If you experience any symptoms of Omega-3 deficiency or struggle with mood disorders, consider boosting your intake through diet or supplementation. This simple step could make a significant difference in your brain function and mental clarity.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional regarding any mental health concerns.