Impact of Olive Oil on Blood Pressure: What the Research Says
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Dietary modifications are a key component of managing blood pressure, and a growing body of evidence points to the potential benefits of olive oil. Let's dive into the scientific findings and explore the mechanisms behind olive oil's possible blood-pressure-lowering effects.
Types of Olive Oil
It's important to understand the different types of olive oil available:
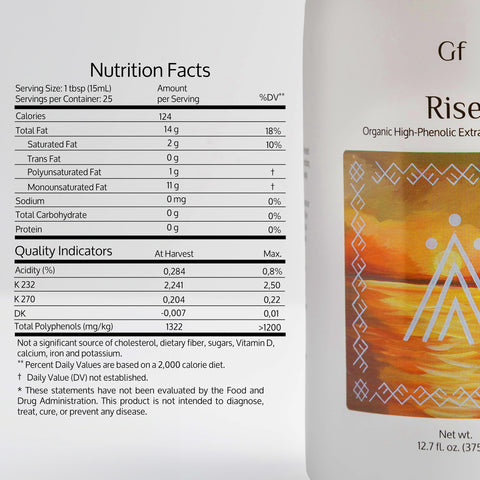
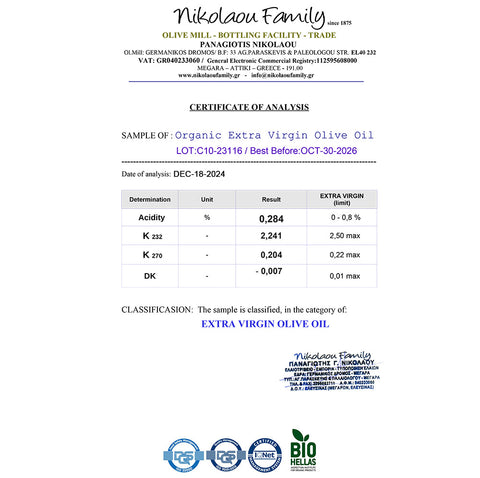
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO): This is the least processed form and boasts the highest concentration of polyphenols, antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits.
- Virgin Olive Oil: Slightly less pure than EVOO, but still considered healthy.
- Pure Olive Oil or Olive Oil: A blend of refined and virgin olive oils, lower in polyphenols.
- Light Olive Oil: Highly refined with mild flavor; its health benefits may be less pronounced.
Most blood pressure research focuses on extra virgin olive oil due to its rich antioxidant content.
Research Highlights
Here's a summary of key findings:
- Reduced Blood Pressure: Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials suggest a modest, but significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure with olive oil consumption. This effect appears stronger with EVOO. [1, 2]
- Comparable to Medication: Some studies indicate that the blood-pressure-lowering effects of a diet rich in polyphenols from olive oil can be similar to specific blood pressure medications. [3]
- Dose and Duration: Benefits seem to increase with higher intake (approx. 15-40g daily) and longer duration of consumption.
Potential Mechanisms
How might olive oil influence blood pressure? Several mechanisms are likely at play:
- Improved Vasodilation: Polyphenols in olive oil may promote nitric oxide production, a compound that helps blood vessels relax and widen, improving blood flow. [4]
- Reduced Inflammation: Olive oil's anti-inflammatory properties could counteract chronic inflammation, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure. [5]
- Healthier Cholesterol Profile: Olive oil's monounsaturated fats may help lower 'bad' LDL cholesterol and raise 'good' HDL cholesterol, improving overall cardiovascular health.
Incorporating Olive Oil & Considerations
- Aim for EVOO: Choose extra virgin olive oil for its maximum health impact.
- Use it Liberally: Drizzle on salads, cooked vegetables, or use for cooking.
- Part of a Healthy Pattern: Olive oil works best as part of an overall balanced diet like the Mediterranean diet.
- Individual Response: Effects may vary. Monitor your blood pressure if you introduce olive oil into your diet.
References
[1] Olive oil and blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
[2] Effects of Olive Oil on Blood Pressure: Epidemiological, Clinical, and Mechanistic Evidence
[4] Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Health
[5] Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammation: A Review of the Evidence and Biological Mechanisms
Disclaimer: This information is not a substitute for personalized medical advice. Always consult your doctor about managing blood pressure, especially if you have hypertension.