Mental health conditions such as depression affect millions of people worldwide. While traditional therapies and medications are essential for many, a growing body of research suggests a connection between omega-3 fatty acids and improved symptoms of depression. Let's explore what these essential nutrients are and how they might be a potential complementary tool in managing depression.
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are considered "essential" because our bodies don't produce them independently. We need to obtain them through our diets. There are three main types:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid): Found in plant sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and vegetable oils.
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid): Primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, sardines, and mackerel.
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): Also found in fatty fish and algae.
The Link Between Omega-3s and Depression
While the science surrounding omega-3s and depression is still developing, here's what we know so far:
- Brain Health: Our brains have a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids. They play a crucial role in brain cell health and communication. Some studies suggest that low levels of omega-3 fatty acids might be linked to an increased risk of depression.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties. Research indicates that chronic inflammation may play a role in the development of depression. [1]
- Neurotransmitter Support: Omega-3s potentially impact the activity of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are involved in mood regulation. [2]
Research on Omega-3s and Depression
Although more research is needed, several studies suggest a potential benefit of omega-3s for depression:
- A meta-analysis of 26 studies found that omega-3 supplements had a statistically significant, though modest, positive effect on depressive symptoms. [3]
- Other studies suggest that EPA-rich omega-3 supplements may be particularly beneficial for those with major depressive disorders. [4]
Adding Omega-3s to Your Diet
Here's how to boost your omega-3 intake:
- Fatty Fish: Aim for 2-3 servings of fatty fish per week.
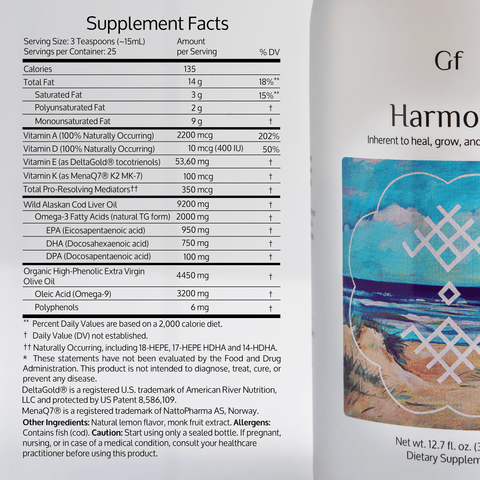
- Omega-3 Supplements: Talk to your doctor about using a high-quality fish oil (check out our Harmony™) or algae-based omega-3 supplement, especially if you don't eat much fish.
- Plant-based Sources: If you're vegetarian or vegan, include ALA-rich foods in your daily diet.
Important Considerations
- Omega-3s are generally safe but discuss potential side effects and interactions with your doctor, particularly if you're taking any medications.
- Omega-3 supplements should never replace prescribed treatment plans for depression. If you're experiencing symptoms, it's crucial to seek professional help.
The Bottom Line
While omega-3 fatty acids shouldn't be viewed as a sole treatment for depression, the research is promising. Boosting your intake of these essential nutrients might offer a complementary benefit in managing mood and promoting overall well-being.
References
[1] Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Depression: A Review of the Evidence and Biological Mechanisms
[2] The Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Neurotransmitters
[3] [Efficacy of omega-3 PUFAs in depression: A meta-analysis]
[4] Omega-3 fatty acids for depression in adults
Disclaimer: This blog post provides general information only. Always seek professional advice for any mental health concerns.