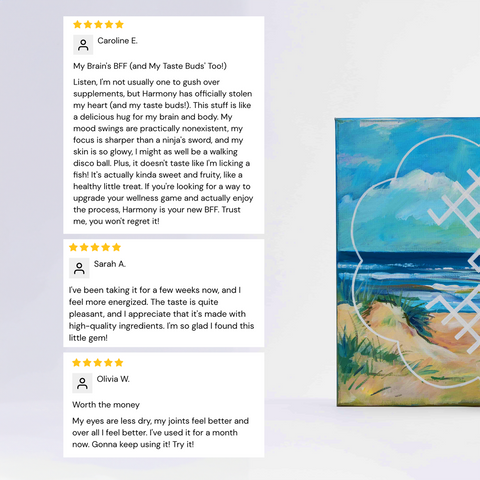
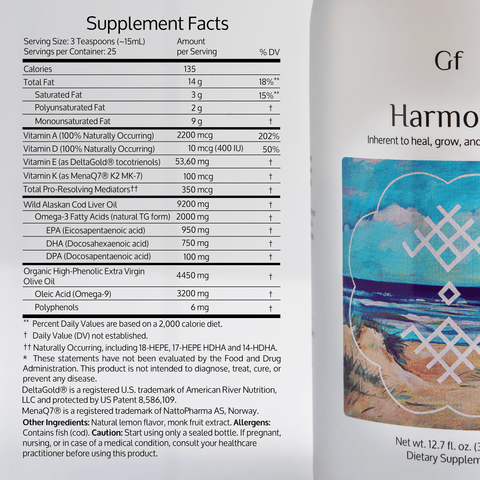
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a key role in brain function, heart health, and reducing inflammation. With countless omega-3 supplements available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you select the best omega-3 supplement for your needs, backed by science.
1. Understand the Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids come in three primary forms:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Found in marine sources, EPA is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can help manage cardiovascular and joint health (source).
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Also from marine sources, DHA is critical for brain and eye health (source).
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): A plant-based omega-3 found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. ALA must be converted to EPA and DHA in the body, but this process is inefficient (source).
For most health benefits, prioritize supplements high in EPA and DHA.
 2. Decide Between Fish Oil and Algae-Based Omega-3
2. Decide Between Fish Oil and Algae-Based Omega-3
Fish Oil
- Extracted from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and anchovies.
- High in EPA and DHA.
- Best for individuals looking for a potent omega-3 source.
Algae-Based Omega-3
- Derived from microalgae, making it a sustainable and vegan option.
- Typically higher in DHA than EPA
3. Look for the Right Dosage
The amount of omega-3 you need depends on your health goals:
- General Wellness: 1100–1600 mg of combined EPA and DHA for adults daily (source).
- Heart Health: 1 gram of EPA and DHA daily (source).
- Joint Pain and Inflammation: 2000–3000 mg daily of EPA and DHA may reduce symptoms of arthritis and improve joint health (source).
Check the supplement label to ensure it meets your required dose without excessive fillers.
 4. Opt for High-Quality Omega-3 Sources
4. Opt for High-Quality Omega-3 Sources
When choosing an omega-3 supplement, prioritize purity and sustainability:
- Purity: Look for molecularly distilled fish oils that remove heavy metals and other contaminants.
- Sustainability: Choose products certified by organizations like Friend of the Sea or MSC (Marine Stewardship Council).
- Example: Goodfatts Alaskan Cod Liver Oil is sustainably sourced and rich in EPA and DHA.
5. Know the Different Forms of Omega-3
Omega-3 supplements come in various forms, affecting absorption and effectiveness:
- Triglyceride Form: Closest to the natural form found in fish, offering better bioavailability (source).
- Ethyl Ester Form: A processed form that may be less bioavailable but still effective.
- Phospholipid Form: Found in krill oil, offering high absorption rates and added antioxidants like astaxanthin.
6. Check for Added Vitamins and Antioxidants
Some omega-3 supplements include additional nutrients:
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health and immune function, often paired with omega-3 since it's a fat-soluble vitamin.
- Antioxidants: Tocopherols (vitamin E) or astaxanthin can protect the oils from oxidation, improving shelf life.
7. Watch Out for Common Omega-3 Supplement Pitfalls
Oxidation and Rancidity
Oxidized fish oils lose potency and may harm health. Ensure your supplement:
- Has a fresh smell (not fishy)
- Includes antioxidants to prevent rancidity
Side Effects
High doses can cause digestive upset or interact with blood-thinning medications. Consult your doctor if you’re taking more than the recommended dose.
8. Read Labels Carefully
Ensure the supplement provides:
- High EPA and DHA content per serving.
- Minimal fillers or unnecessary additives.
- Clear sourcing information for transparency.
9. Takeaways for Choosing the Right Omega-3 Supplement
- Determine Your Needs: General wellness, heart health, or specific conditions like high triglycerides.
- Focus on EPA and DHA: Choose supplements with high concentrations of these omega-3s.
- Prioritize Quality: Look for purity, sustainability, and bioavailability.
By choosing the right omega-3 supplement, you can support your health goals effectively and sustainably.