Olive oil has long been celebrated for its health benefits, but myths surrounding its use in cooking can leave people confused. Is olive oil safe for high-heat cooking? Does it lose its nutrients when heated? Let’s separate fact from fiction and uncover the truth about cooking with olive oil, backed by scientific evidence.
Myth 1: Olive Oil Has a Low Smoke Point and Isn’t Suitable for Cooking
Fact: The smoke point of olive oil depends on its quality. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has a smoke point between 375°F and 410°F (190°C–210°C), making it suitable for most cooking methods, including sautéing and baking.
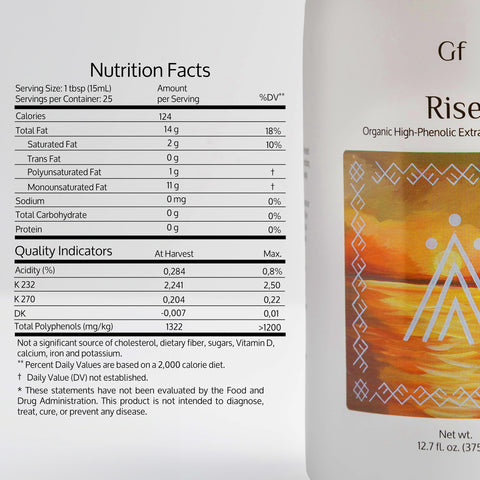
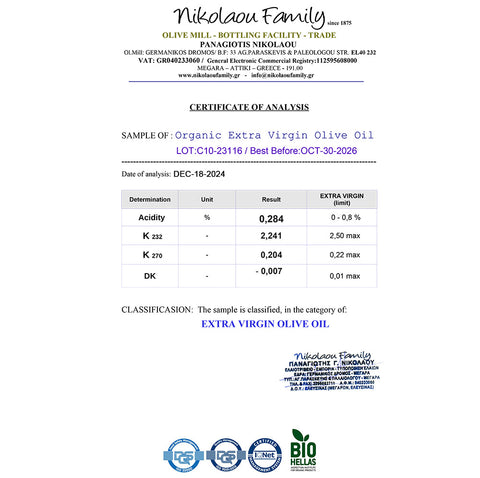
A study published in Trends in Food Science & Technology showed that EVOO remains stable at typical cooking temperatures, retaining its antioxidants and beneficial compounds even when exposed to heat (source). While high-heat frying may degrade some of its polyphenols, the oil's healthy fats remain intact.
 Myth 2: Heating Olive Oil Destroys Its Nutritional Value
Myth 2: Heating Olive Oil Destroys Its Nutritional Value
Fact: While prolonged high-heat exposure can reduce some of olive oil’s polyphenols, its core nutritional value, including monounsaturated fats, remains largely intact.
Research in the Journal of Food Chemistry demonstrated that EVOO maintains a significant portion of its antioxidants and stability even at frying temperatures (source). EVOO is more heat-stable than many refined oils due to its natural antioxidant content.
Myth 3: You Should Only Use Olive Oil for Salad Dressings
Fact: Olive oil isn’t just for cold dishes—it’s versatile and perfect for cooking. It can be used in stir-frying, roasting, and even grilling. Its rich flavor enhances dishes without breaking down at moderate cooking temperatures.
A 2020 study in Antioxidants found that olive oil’s polyphenols are resilient during cooking, providing both flavor and health benefits to heated dishes (source).
Myth 4: Cooking with Olive Oil Produces Harmful Compounds
Fact: Compared to many refined vegetable oils, olive oil produces fewer harmful compounds when heated. Its monounsaturated fats are more stable than the polyunsaturated fats found in seed oils like canola or sunflower oil.
A study in Food Chemistry revealed that olive oil releases fewer volatile aldehydes, a type of harmful compound, compared to other oils when exposed to heat (source). This makes olive oil a safer choice for cooking.
 Myth 5: You Need Special "Cooking Olive Oil"
Myth 5: You Need Special "Cooking Olive Oil"
Fact: High-quality extra virgin olive oil works perfectly for cooking, contrary to the belief that only refined olive oil is suitable for heat. While refined olive oil has a higher smoke point, EVOO retains more nutrients and flavor, even during cooking.
A recent 2021 study highlighted that EVOO performs well under heat due to its antioxidant content, making it a healthier choice than refined oils (source).
Best Practices for Cooking with Olive Oil
To get the most out of olive oil, follow these tips:
- Use EVOO for Medium-Heat Cooking: Ideal for sautéing, roasting, and baking.
- Store Properly: Keep your olive oil in a dark, cool place to preserve its nutrients.
- Avoid Overheating: If the oil starts to smoke, lower the heat to prevent degradation.
Why Olive Oil Is Still the Best Choice
Olive oil’s blend of healthy fats and antioxidants makes it a superior choice for cooking. While some degradation occurs at extremely high temperatures, olive oil remains more stable and healthier than most other cooking oils.