Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for overall health, providing numerous benefits for the heart, brain, and joints. However, despite the well-known health advantages, many people fall short of the recommended daily intake of these essential fats. In this post, we’ll explore the average intake of Omega-3s in different populations, why it matters, and how supplementation can help bridge the gap for optimal health.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids essential for the human body. The most important types are:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Known for its anti-inflammatory properties and heart health benefits.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Crucial for brain development, cognitive function, and vision.
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Found primarily in plant-based foods, ALA needs to be converted into EPA and DHA, but this process is not very efficient in the body.
Omega-3s are considered essential fats, meaning the body cannot produce them on its own and must obtain them through diet or supplements.
What Is the Recommended Daily Intake of Omega-3s?
Health organizations recommend different daily intakes of Omega-3 fatty acids depending on age, gender, and health condition:
- Adults: Most health organizations recommend a minimum of 250–500 mg combined EPA and DHA every day for adults (source). This can be obtained from about 8 ounces of fatty fish per week. However, higher amounts are often recommended (source).
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: Research shows that Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, are vital before, during, and after pregnancy (source). Most official guidelines recommend adding 8–12 ounces of fish per week during pregnancy and nursing, or an extra 200–300 mg of DHA per day (source).
-
Children: Omega-3s are vital for children's brain and eye development, with recommendations varying based on age and weight, but around extra 200-300 mg of DHA per day is often suggested (source). The FDA suggests regular fish or seafood intake for children. Serving size depends on age (source):
- 1 ounce at ages 1–3
- 2 ounces at ages 4–7
- 3 ounces at ages 8–10
- 4 ounces at age 11 and up
However, studies show that many people do not meet these recommended levels through diet alone. According to a study published May, 2021 in BMJ Open, it was discovered that more than 60% of adults in the United States and 95% of children in the United States do not meet their nutritional needs for Omega-3 fatty acids (source).

Average Omega-3 Intake Around the World
Despite the known benefits of Omega-3s, the average intake varies widely depending on location, diet, and lifestyle.
- Western Diets: In countries like the United States, Canada, and much of Europe, the average intake of Omega-3s is significantly lower than recommended. The typical Western diet is high in Omega-6 fatty acids (found in processed foods and vegetable oils) and low in Omega-3s, which can lead to an unhealthy imbalance (source).
- Mediterranean Diet: People in Mediterranean regions typically consume higher levels of Omega-3s due to their diet rich in fish, olive oil, and other healthy fats. This population often meets or exceeds the recommended daily intake (source).
- Asian Diets: In some Asian countries like Japan, Omega-3 intake is also higher, thanks to the frequent consumption of fatty fish. This contributes to the lower rates of cardiovascular disease in these populations (source).
Unfortunately, the modern diet in many developed countries lacks sufficient Omega-3s, which can negatively impact health in the long term.
Why Supplementation Is Important
For those who struggle to get enough Omega-3s through diet alone, supplementation is an easy and effective way to ensure you meet your daily needs.
1. Heart Health Support
Numerous studies have shown that Omega-3 supplementation can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. EPA and DHA help lower triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and even lower blood pressure (source). For those with a low intake of fish or other Omega-3-rich foods, supplements are vital for maintaining heart health.
2. Brain and Cognitive Function
DHA, a key component of Omega-3s, is essential for brain function. Supplementing with DHA has been linked to improved cognitive performance, memory, and even a reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease (source). Omega-3s also support mental health, as studies have suggested that higher intake of these fats may help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety (source).
3. Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including arthritis, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune diseases. EPA and DHA are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, and supplementing with Omega-3s can help manage inflammation and improve joint health (source).
4. Eye Health
DHA plays a critical role in eye health, particularly in maintaining the retina. Studies have shown that higher levels of Omega-3s can reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and dry eye syndrome (source).

5. Omega-3 Deficiency Is Common
Unfortunately, Omega-3 deficiency is common, particularly in countries where fish consumption is low. Signs of Omega-3 deficiency can include fatigue, poor memory, dry skin, heart problems, mood swings, and joint pain. Regular supplementation helps prevent these symptoms and promotes overall well-being.
How to Supplement Omega-3s Effectively
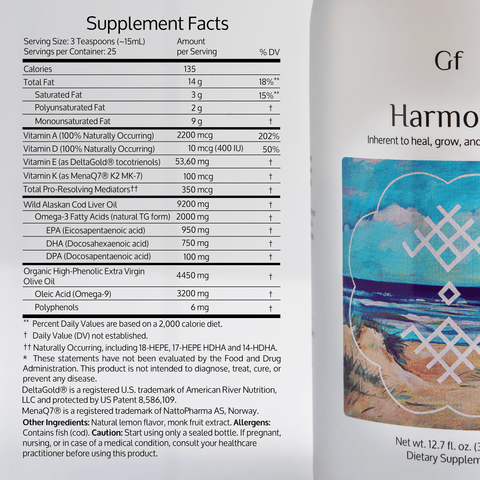
To ensure you’re getting enough Omega-3s, look for high-quality fish oil or algae-based supplements. Check that they contain both EPA and DHA, as these are the most beneficial forms of Omega-3s.
- Fish Oil: Derived from oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, fish oil supplements are the most popular and potent source of Omega-3s.
- Algal Oil: A vegan alternative, algal oil is sourced from algae and provides a plant-based way to get DHA and EPA.
- Krill Oil: This option is rich in Omega-3s and antioxidants like astaxanthin, which helps protect the fatty acids from oxidation.
When choosing a supplement, opt for one that has been third-party tested for purity and is free from harmful contaminants like mercury or other toxins.
Conclusion
While Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for many aspects of health, the average intake across much of the world falls short of the recommended levels. This deficiency can have serious health consequences over time. By understanding the importance of Omega-3s and incorporating them into your diet—whether through food sources or supplementation—you can support heart health, brain function, inflammation control, and more. If your current diet lacks Omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, supplements are a convenient and effective way to ensure you’re getting the right amount to support your long-term health.